Press release: Fish stocks boost for endangered pearl mussel
Thousands of sea trout have been released into rivers in Northumberland to stock rivers for anglers and help protect the future of a critically endangered species, the freshwater pearl mussel.
Pearl fishing and water pollution from industry have led to worldwide decline of the pearl mussel.
A healthy population of endangered freshwater pearl mussels is important for water quality – each mussel filters 50 to 70 litres of water. They improve the quality of the habitat, increasing the ecological diversity, which includes juvenile trout and salmon numbers.
The Environment Agency’s Kielder Salmon Centre staff Richard Bond and Jess Anson have developed a technique to enable pearl mussel larvae to attach to the fish gills, replicating their natural life cycle in the wild.
The larvae will drop off the sea trout gills towards the end of May where they will settle on to the river bed. Given the right conditions, these juveniles could survive into adulthood and live for up to 100 years.
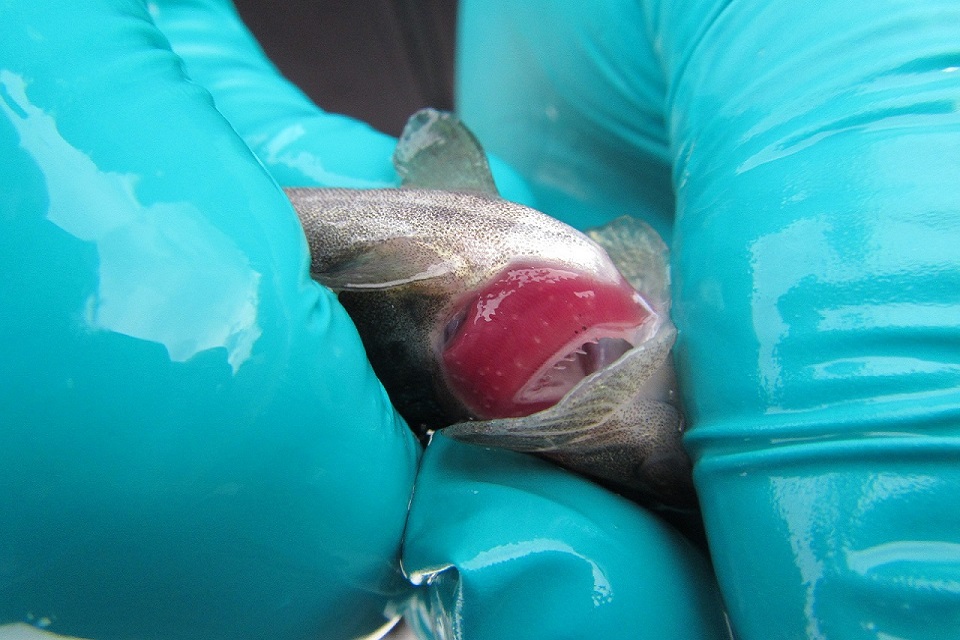
Around 12,000 one-year-old sea trout, which have been bred at Kielder Salmon Centre, were released this week into North Tyne tributaries of the River Tyne.
The larvae attached to them were harvested from 80 adult mussels which are cared for at the centre.
Kielder Salmon Centre breeds 360,000 salmon and between 10,000 and 20,000 sea trout every year to stock rivers.
Complex life cycle
Richard said:
The pearl mussel has a complex life cycle which begins as larvae. These larvae, called glochidia, requires salmon or sea trout to host them for the first stage of their development.
They attach to the gills of trout in the River Tyne between late July and early August, where they remain until the following spring when they drop off the fish’s gills. They need clean water and gravel, and well oxygenated water where they continue to grow.
The survival rate for juveniles has declined over the years, which has led to an ageing population, with few mussels under 50 years old.
This means they are a critically endangered species with only around 30,000 adult mussels in the wild in the North Tyne area, and 500,000 across the country.
This work at the hatchery is to try to increase the numbers of juveniles in the river, boost future numbers, natural reproduction and survival rates in efforts to halt the population decline.
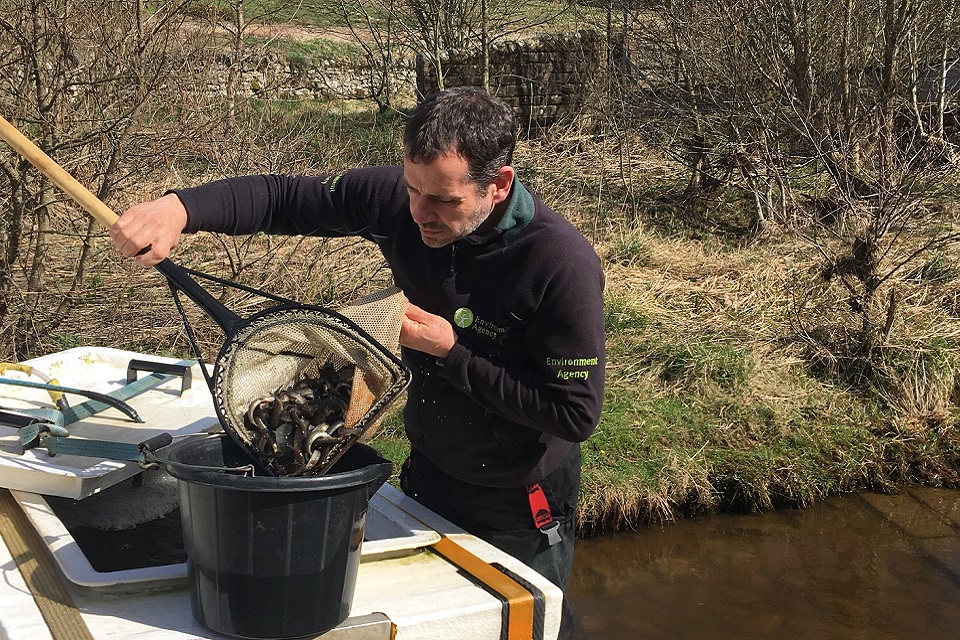

Water quality improvements
After considerable investment, water quality has improved dramatically across the UK and rivers in England are the healthiest they have been for 20 years.
The improvements in water quality of the River Tyne and its tributaries has been excellent, and along with the continued work of the Environment Agency and partners, has resulted in improved conditions for natural breeding in the rivers, and a flourishing ecology.
Kielder Salmon Centre pearl mussel project
Richard added:
In 2010 we first managed to successfully get freshwater pearl mussel larvae to attach to the gills of sea trout. Since then we have released sea trout every spring to the River Tyne tributaries.
Over the next two years we will be carrying out surveys, looking for the first of these juvenile mussels that were released to see if or where they have survived.
Even at 7 years old they will be less then 3cms long, most of which will be buried under the river bed. In another 7 to 10 years they should be old enough to breed.