His appointment by the Secretary-General back in 2014 was a landmark: he became the first Asian, Muslim and Arab ever to hold the post.
Before that, Zeid had already enjoyed a long and distinguished career, both at the UN and as a Jordanian diplomat. He served his country in several capacities, notably as Ambassador to the United States, and Permanent Representative to the United Nations in New York, with a stint as President of the Security Council in January 2014.
Governments are more than capable of defending themselves. It’s not my job to defend them. I have to defend civil society, vulnerable groups, the marginalized, the oppressed.
Throughout his career, Zeid has demonstrated a commitment to international law, playing a major role in the establishment of the International Criminal Court, as the first President of the Assembly of States Parties to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court – turning the court from an idea into a reality – and, eight years later, overseeing the legal definition of the crime of aggression and the court’s jurisdiction over it.
In his last major interview with UN News, the UN human rights chief tells us that the “real pressure on this job comes from the victims and those who suffer and expect a great deal from us.”
“Governments are more than capable of defending themselves. It’s not my job to defend them. I have to defend civil society, vulnerable groups, the marginalized, the oppressed. Those are the people that we, in our office, need to represent,” he adds, noting that “oppression is making a comeback”.
When asked about whether his view of the UN and what it can achieve has diminished during his time spent speaking out loudly in defence of the abused and defenceless over the past four years, he says:
“It’s very difficult to tolerate abuse of the UN when I keep thinking of the heroic things that people do in the field, whether the humanitarian actors or humanitarian personnel, my human rights people, the people who are monitoring or observing. And I take my hat off to them. I mean, they are the UN that I will cherish and remember.”
UN News: When you compare the human rights landscape today to when you took over the UN human rights office back in 2014, what are the key differences that you see?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: When I took over, it coincided with the terrible videos put online by Daesh, or ISIS, which stoked a great deal of fear and horror. And we began to see a sort of a deepening of the crisis in Syria and in Iraq. And this then folded into two things:
One, a great determination to embark on counter-terrorism strategies, which we felt were, in part, excessive in certain respects. Every country has an obligation to defend its people, and the work of terrorism is odious and appalling and needs to be condemned and faced. But whenever there is excessive action, you don’t just turn one person against the State, you turn the whole family against the State. Ten or maybe more members could end up moving in the direction of the extremists.
And then, the migration debates, and the strengthening of the demagogues and those who made hay out of what was happening in Europe for political profit. As each year passed, we began to see a more intense pressure on the human rights agenda.
UN News: You have been very outspoken and you’ve called out governments and individual leaders around the world who have abused human rights. Do you see that as the most important role for the UN human rights chief?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: Yes. At the Human Rights High Commission, you’re part of the UN, but also part of the human rights movement and both are equally important. As I said on earlier occasions, governments are more than capable of defending themselves. It’s not my job to defend them. I have to defend civil society, vulnerable groups, the marginalized, the oppressed. Those are the people that we, in our office, need to represent.
I always felt that that is the principle task: we provide technical assistance, we collect information, we go public on it. But in overall terms, the central duty for us is to defend the rights of those most marginalized and those that need it.
UN News: what if you come under pressure to stay silent?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: Well, the interesting thing is that the pressure on this particular job doesn’t really come very much from the governments. They all attack the office because we criticize all of them, but we also point to areas where there is improvement, and I sometimes will praise the government for doing the right thing.
The real pressure on this job comes from the victims and those who suffer and expect a great deal from us. That’s the pressure that I think matters most in terms of the need to do the right thing.
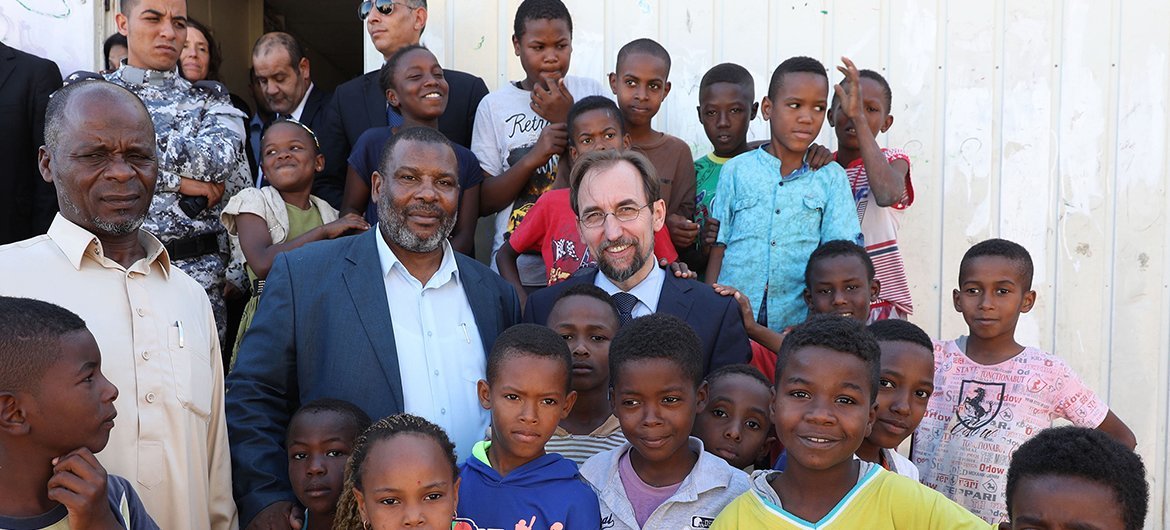

UNSMIL/Abel Kavanagh
UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein, during an official mission to Libya. Tripoli, Libya, 10 October, 2017.
UN News: Have there been times, therefore, when you’ve had to compromise a bit too much and maybe even let rights campaigners down in some way?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: No, not in that sense because I think I’ve been outspoken enough and I think I broke new ground when it came to High Commissioners. I can tell you in almost every meeting I sit with governments and I say things that I know they would never have heard before from someone in the UN.
No, the enormity of the suffering of people creates a feeling of inadequacy that, no matter what I do —an interview like this, a press conference, a report — it’s not going to restore a disappeared son or daughter to his or her mother. I know it won’t end the practice of torture immediately. I know that the residents in an IDP [Internally Displaced Peoples] camp, are not going to next day be moved into something more improved.
And that feeling is the pressure that I’m speaking about. It’s this sort of feeling that no matter what I do, it’s unequal to the colossal challenge that stands before us.
UN News: Have there been times when you thought it best to use quiet diplomacy to work behind the scenes?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: We’re always trying. We’re always trying to use quiet diplomacy. I mean, we’re constantly meeting with governments, and I send letters, and we conduct phone calls.
But on occasion we make a determination that we’ve tried these tracks, it hasn’t worked, and that I’m going to go public. Sometimes, I asked my spokesperson to do it; sometimes, I ask my regional office to do it; and other times, I’ll do it myself. But it’s carefully thought through.
There was one foreign minister, for example, I needed to speak to. We were planning to send a technical mission to his country and, for almost a year, he avoided me. I saw him here in the GA [General Assembly] and he said, “Yes, yes, yes,” and then just avoided me. So then, we got a message to him that I’m going to go public tomorrow, and he was on the phone right away.
And the lesson learned was that if you don’t sometimes threaten to speak out, you don’t grab their attention. And I would rather err on the speaking out part than staying silent.
I first worked with the UN in 1994, 1995 in the former Yugoslavia. And I saw what catastrophes silence can bring. And I think from that point on, I was determined not to be silent when the evidence before us was presented.
UN News: What’s touched you most personally in the job? What have been those moments, the encounters with people that have meant the most to you?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: There have been many. I think it’s very hard to listen to the suffering of people. One of the times was when I went to the Ilopango detention centre in El Salvador. [Four young women] had been sentenced to 30 years in prison. They claimed these were obstetric emergencies: miscarriages. The State claimed that these were terminations of pregnancy.
When I sat with them – I had with me a full team, my office, assistants and interpreters – I think within the space of about 10 minutes we were all weeping; we were in tears because their suffering was so extreme. One of them was telling us how her foetus was on the ground and rather than take her to a hospital, they handcuffed her and took her to prison. And I thought the cruelty, the capacity for human cruelty is amazing.
I saw the president after that and I said, “Why is it that all these girls are poor? Every single one of them?” It’s as if it’s only the poor that face these sorts of conditions. This is the point that really strikes home that time and again: the poor suffer all the consequences. And that for me was a moment that will always remain with me. And there have been quite a few like that.
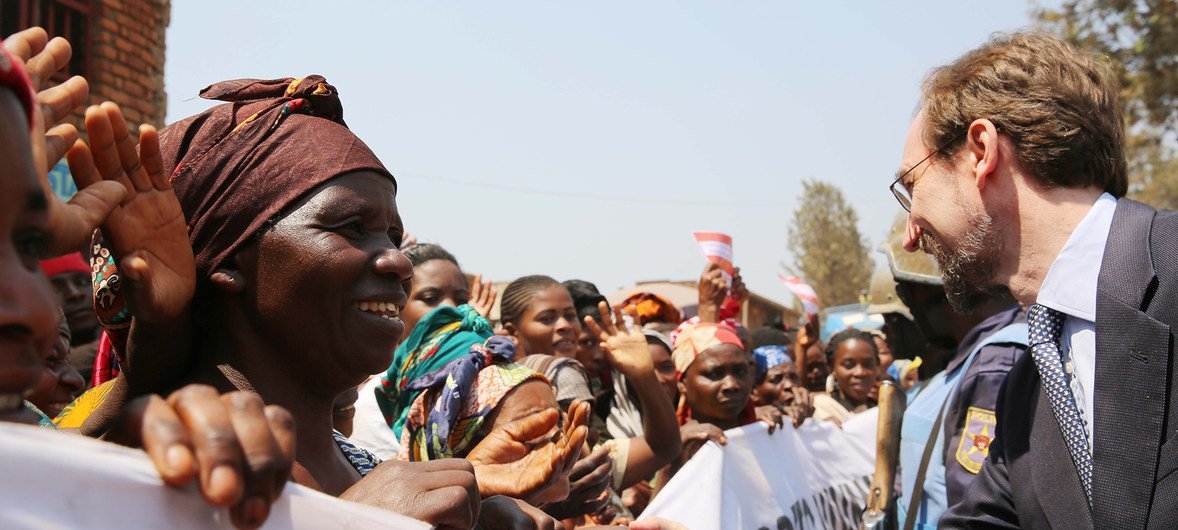

OHCHR
UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein, meeting women during a visit to the Panzi hospital, in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, July 2016.
UN News: Is there a specific moment that stands out as being the most difficult or perhaps even the most consequential during your tenure?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: It’s all been difficult. When you’re defending the rights of people, and there’s so much pressure exerted upon you from this deep inner need or desire to help them, it’s all quite tough.
But I take inspiration from the amazing human rights defenders, journalists, lawyers, activists in so many countries who do amazing, brave things to highlight the plight of others; to defend the rights of others. Whatever I may want to complain about day in, day out, it’s nothing compared to the pressure that these people face, confront, overcome — often they have no fear.
These are the real leaders; these are the people that inspire. Not many of the politicians who claim to be leaders and are weak and self-serving, and are leaders in name only. The real leaders are the ones who, against all odds, will do the right thing and then often pay a price for it, and be detained for it.
And I think that’s what keeps us fuelled and working on their behalf.
Again, the point to be made is that, yes, we are part of the UN, but we’re also part of a human rights movement. The UN is creating order amongst States: with us, we look at the heart of the relationship between the governing and the governed and so, of course, it’s going to be sensitive.
People have their rights, the States have their obligations, their commitments. And we have to defend the people.
UN News: Where do you think you’ve made the biggest difference, personally? And have you made mistakes?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: I don’t know. The question ought to be addressed to civil society, victims’ groups, human rights defenders. And if they said, “Zeid has done a good job,” I’d be very content with that. If they said, “Zeid could have done better,” I’d have to learn to live with it and accept it. It’s really for them to quantify the extent to which I have achieved something or whether they think that I was able to undertake my responsibilities in the right manner.
UN News: you said that being High Commissioner for Human Rights is a unique job within the UN, and you seem to have followed a fairly similar path to your predecessors in making yourself unpopular with governments. Do you want to see your successor sticking to that path?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: The fundamental point that I mentioned earlier is that the States can defend themselves. Our job is not to defend the States, and the law is there for the protection of the weak, not in defence of the strong.
And so, we look at the law, we look at the obligations of States, and our job is to defend the individual victims, vulnerable communities, marginalized communities, or oppressed communities.
Oppression is making a comeback. Repression is fashionable again.
And so, I don’t believe anyone holding this position — even if they felt differently — can ultimately conduct business in a manner that departs too radically from the way that I, or my predecessors, have done it. If you try to depart, it will be extremely unpleasant for you because you’re going to hear it from the very people who are suffering. And there can be nothing that will tear at your conscience more, if you abandoned them. So, my belief is that the job defines the conduct.

UN Photo/Jean-Marc Ferre
UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein, at the 38th Regular Session of the Human Rights Council. 18 June 2018.
UN News: Is there any other key advice you’d give?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: I would always say be in good health because it is a demanding job, and it is taxing. Whoever takes this job has to be ready for it. Some jobs in the UN system are viewed as sinecures, retirement posts for national officials. This is not one of them. This requires complete commitment.
UN News: For you, where to next? And as a seasoned ex-diplomat with so much UN experience, how has doing this job changed your view of the world?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: I don’t know, maybe I’ll be a journalist!
I’ve been away from my family; I need to spend time with them and then I’ll look and see what new direction I’d want to take myself. But I need a rest as well.
UN News: having walked this tightrope, do you feel perhaps a little more appreciative of what the UN does, or perhaps a little less?
Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein: No, if I were to, in the future, think of the UN, I would think of the moments in the field where I see the UN doing amazing things.
It’s very difficult to tolerate abuse of the UN when I keep thinking of the heroic things that people do in the field, whether they be humanitarian personnel, my human rights people, the people who are monitoring, observing, with some threat to themselves: I take my hat off to them. They are the UN that I will cherish and remember.
To the outside world, the jargon, the terminology, seems inaccessible. I think that the work that UN personnel do in the field is much more understandable. That’s how I entered the UN, in the field, and that’s how I got to know it. And I think that’s where the UN has enormous impact and needs to continue to make the investment and do the right thing.
And you can also hear Zeid articulating his passion for international justice in a recent UN News podcast in which he interviewed Ben Ferencz who, at 99 years of age, is the last surviving prosecutor of the post-war Nuremberg military tribunals and was one of the leading campaigners for an international court.